The Importance of Sleep for Mental Wellness
Sleep is a fundamental component of overall health and well-being, particularly when it comes to mental wellness. The relationship between sleep and mental health is complex and bidirectional; poor sleep can exacerbate mental health issues, while mental health problems can lead to sleep disturbances. Understanding this relationship is crucial for promoting better mental health outcomes.
1. Sleep’s Role in Emotional Regulation
During sleep, particularly during the rapid eye movement (REM) stage, the brain processes emotional information and consolidates memories. This process is vital for emotional regulation. Insufficient or poor-quality sleep can impair this function, leading to increased negative emotional responses to stressors and decreased positive emotions. As a result, individuals may find it more challenging to cope with daily stressors, which can contribute to anxiety and depression.
2. Bidirectional Relationship Between Sleep and Mental Health
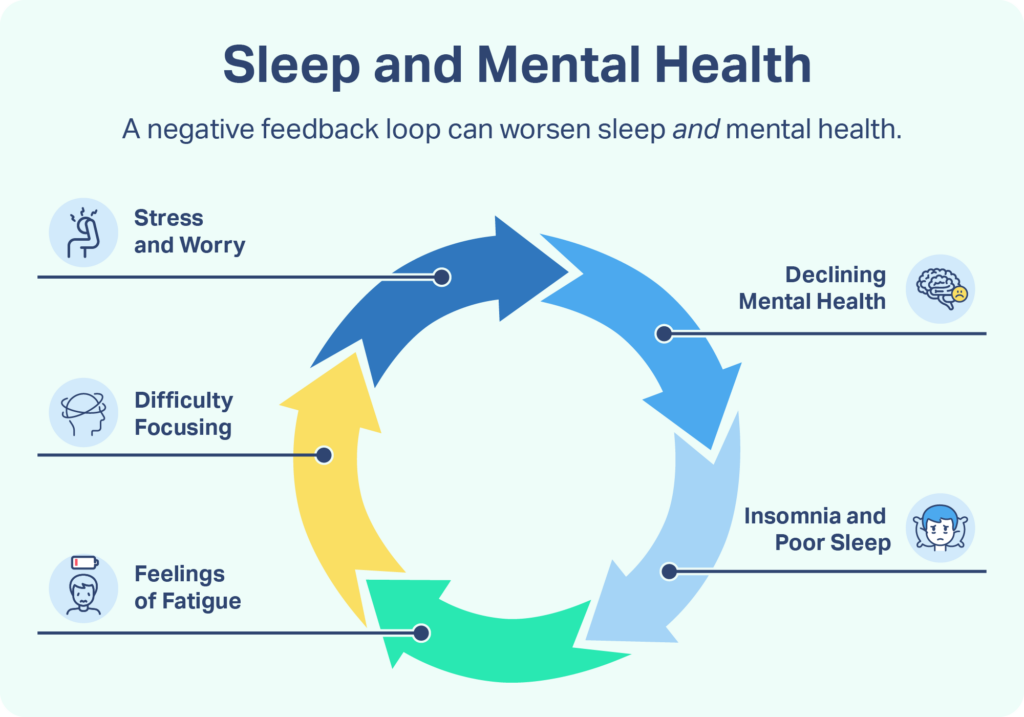
Research indicates that there is a bidirectional relationship between sleep and various mental health conditions. For instance, insomnia is commonly observed in individuals with depression, anxiety disorders, bipolar disorder, and PTSD. Conversely, chronic sleep deprivation can increase the risk of developing these conditions or worsen existing symptoms. This cycle creates a negative feedback loop where poor sleep exacerbates mental health issues, which in turn leads to further sleep disturbances.
3. Impact on Cognitive Functioning
Quality sleep is essential for cognitive functions such as attention, learning, memory consolidation, decision-making, and problem-solving skills. Lack of adequate sleep can impair these cognitive abilities significantly. Individuals may experience difficulties in focusing or making decisions when they are sleep-deprived. This impairment not only affects personal productivity but also impacts social interactions and relationships.
4. Increased Risk of Mental Health Disorders
Studies have shown that insufficient sleep increases the risk of developing various mental health disorders including depression and anxiety. For example, approximately 75% of individuals with depression report experiencing insomnia symptoms. Furthermore, chronic insomnia has been linked to an increased risk of suicidal ideation among those with pre-existing mental health conditions.


It's Not About Being the Best! It's About Being Better Than You Were Yesterday. Don’t Punish Yourself with HSV Or Other Viruses Just Because You Don’t Believe You Can Get Rid of It or Just Because You Don’t Know of a Possible Cure
ReplyDeleteReach out to dr asha osemudiamen to get a Powerful Herbal Remedy Which Treat and Eliminate STDS Completely Without Any Side Effect.
Contact dr asha osemudiamen via +1 (469) 278-5369
Email: drashaosemudiamen@gmail.com
https://wa.me/+14692785369
Hello, I want to write a little
ReplyDeletereview about the good work of Asha healing hand herbs who cured me
from HSV 1&2 for 2 weeks
with his herbs
Call or text to purchase yours +14692785369
https://drashaosemudiamen1.wixsite.com/naturaherbalmedicine
Health Horoscope - Today’s health horoscope encourages nurturing your body and mind with balanced habits. Eat wholesome meals and stay hydrated to maintain vitality. Light exercise, such as walking or yoga, will boost flexibility and mood. Avoid overexertion and take short breaks to recharge. Restful sleep and positive thinking enhance overall wellness and immunity. Visit: Horoscope | Astrology
ReplyDelete